In the fast-evolving world of online shopping, Flipkart’s journey from a small online bookstore to a major e-commerce player serves as a testament to the power of innovation and customer-focused strategies.
In India, there are many e-commerce platforms, but one stands out for its fast growth and popularity—Flipkart. Founded in 2007 by Sachin and Binny Bansal, Flipkart began as an online bookstore. Today, it’s one of the biggest e-commerce platforms in India, changing the way millions of people shop online.
In 2018, Walmart bought Flipkart for $16 billion, showing just how successful it has become. So, what makes Flipkart so successful? How does it make money and stay ahead of others?
In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at Flipkart’s business model, how it earns revenue, and how it became a leader in India’s e-commerce industry.
Flipkart: A Brief Overview
Flipkart operates on a Business-to-Consumer (B2C) model, which connects sellers with buyers. The platform allows millions of customers across India to buy a wide variety of products ranging from electronics to groceries, clothing, home goods, and much more. Through its marketplace, Flipkart doesn’t just sell products but facilitates transactions between buyers and sellers.
One of Flipkart’s biggest strengths is its ability to provide an easy and convenient shopping experience. It has built a reputation for offering attractive discounts, especially during its famous Big Billion Day Sale, which has become an annual tradition in India, offering massive discounts on products across various categories.
Additionally, Flipkart has expanded its business to include services like PhonePe (a FinTech app), FarmerMart (a food retail business), and Myntra (a fashion e-commerce site), helping it broaden its customer base and revenue streams.
Revenue Generation: How Flipkart Makes Money?
Although Flipkart has faced a reported loss of INR 46,895 Crore in recent years, it still generates substantial revenue through multiple streams.
Let’s take a closer look at how Flipkart keeps the cash flowing.
| Revenue Stream |
| Marketplace Commission |
| Logistics and Fulfillment Services |
| Advertising Revenue |
| Subscription Services (Flipkart Plus) |
| Financial Services (Flipkart Financial Services) |
1. Marketplace Commission
The primary revenue source for Flipkart comes from being a platform that connects sellers with customers. Sellers list their products on Flipkart’s platform and, in return, the company charges a commission on each sale. The commission varies depending on the category of the product and the rating of the seller.
For instance, electronics may carry a different commission than clothes or books. This allows Flipkart to make money every time a product is sold on its platform.
2. Logistics and Fulfillment Services
Flipkart doesn’t just act as a marketplace. It owns a logistics arm called E-kart, which manages the delivery of products to customers. This division provides various services like packaging, storage, and shipping. Flipkart charges sellers a fee for these logistics and fulfillment services, which forms another significant revenue stream.
3. Advertising Revenue
Another way Flipkart generates income is through advertising. The platform allows sellers to promote their products via sponsored listings, banner ads, and other promotional tools. Sellers pay Flipkart to feature their products more prominently, boosting their visibility to a wider audience. Additionally, Flipkart displays third-party ads on its platform, further diversifying its revenue sources.
4. Subscription Services (Flipkart Plus)
To keep customers loyal, Flipkart launched its subscription service Flipkart Plus. This program offers customers various perks like free delivery, early access to sales, and exclusive discounts. Flipkart earns revenue from customers who subscribe to the service, creating another consistent income stream. The Flipkart Plus program not only helps retain customers but also enhances their shopping experience.
5. Financial Services (Flipkart Financial Services)
Through its subsidiary, Flipkart Financial Services, the company provides various financial services like working capital loans, insurance, and invoice financing to its sellers. Flipkart generates revenue from interest charges and fees related to these financial products. By offering financial solutions, Flipkart helps its sellers grow their businesses while also benefiting from the financial services sector.
How Does Flipkart Function?
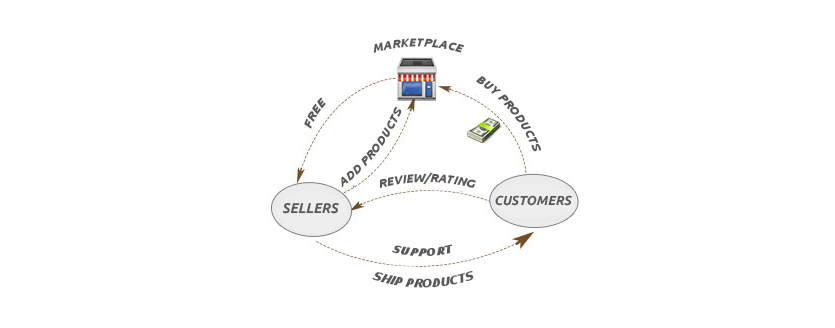
At the core of Flipkart’s operations is its platform.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how Flipkart works:
| Flipkart Operations Breakdown |
| Sellers List Products |
| Customers Browse and Purchase |
| Order Placement |
| Product Delivery |
| Payment and Commission |
| Customer Support |
- Sellers List Products: Vendors or businesses list their products on Flipkart’s platform, providing detailed descriptions, images, and pricing.
- Customers Browse and Purchase: Customers can browse the platform’s extensive catalog of products, filtering based on categories, price, or ratings. Once they find a product they want to buy, they add it to their cart and proceed to checkout.
- Order Placement: Customers place their orders using various payment methods such as credit cards, debit cards, or even cash on delivery.
- Product Delivery: Once an order is placed, Flipkart notifies the seller, who ships the product through Flipkart’s logistics network. Flipkart handles packaging and delivery, ensuring the product reaches the customer’s doorstep efficiently.
- Payment and Commission: After the product reaches the customer and they confirm delivery, Flipkart processes the payment. It deducts its commission from the seller’s earnings and transfers the remaining amount to the seller.
- Customer Support: Flipkart provides a customer service team to handle any issues with products, returns, or exchanges. The company is known for its flexible return policy, which builds customer trust and satisfaction.
Flipkart’s Digital Marketing Strategy
Flipkart has mastered the art of digital marketing to build its brand and reach millions of customers. Here are some key aspects of its strategy:
- Social Media Marketing: Flipkart actively engages with customers through platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, using these channels to promote products, announce deals, and share customer success stories.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Flipkart invests heavily in optimizing its website to rank higher on search engines. This helps the platform attract more organic traffic from users looking for products online.
- Email Marketing: Flipkart uses email campaigns to notify customers about new arrivals, ongoing sales, and exclusive discounts, which helps drive repeat purchases.
- Influencer Marketing: Flipkart partners with social media influencers and celebrities to promote its products, enhancing its brand visibility and credibility among their followers.
- Performance Marketing: Flipkart invests in paid advertising like search ads and display banners to attract potential buyers, using advanced targeting strategies to maximize the effectiveness of its ads.
Other Revenue Channels for Flipkart
In addition to the core revenue streams mentioned above, Flipkart also generates income through:
- Co-Branding and Advertising Opportunities: Flipkart offers advertising space on its homepage and product pages. Brands can co-advertise their products on Flipkart’s platform, paying for these premium spots to gain visibility.
- Myntra: Flipkart owns Myntra, a leading fashion e-commerce platform. Myntra’s revenue contributes to Flipkart’s overall earnings, especially in the fashion and lifestyle categories.
- Targeted Search Results: Flipkart makes money from brands that pay to have their products appear at the top of search results, increasing their chances of being purchased.
Conclusion
Flipkart’s business model has revolutionized the way Indians shop online. By offering a wide range of products, competitive pricing, and a customer-centric approach, Flipkart has become an integral part of India’s e-commerce ecosystem. The company has successfully diversified its revenue streams, from commissions to logistics services, digital marketing, and even financial products.

